Urinary Incontinence – Never Normal
Incontinence refers to the involuntary or unintentional loss of urine, leading to the inability to control bladder. It is a common and often embarrassing problem that can affect people of all ages, but it is more prevalent among older adults.
A hidden condition but it needs to be discussed often
- It is a well-known fact that people are reducing fluid intake and they are self-managing the voiding frequency.
- Nearly two third of patients are symptomatic for two years before seeking the treatment and 30% of patients who are seeking treatment receives no assessment.
- People are also having a fear of leakage and that’s why they are not Comfortable in social gatherings.
Urinary incontinence symptoms
Urinary incontinence is a result of overactive bladder and the overactive bladder symptoms are:
- Eight or more visits to the toilet by 24 hours.
- Urination at night- two or more visits to toilet during sleeping hours.
- Urgency to urinate and it’s a sudden strong desire.
- Sudden and involuntary loss of urine.
What are the risk factors of overactive bladder
- Neurological disease.
- Although both males and females are having this issue, Females are having more prevalence of having overactive bladder symptoms.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Hysterectomy surgery.
- Postmenopausal status.
- Increased age.
There are certain myths and thought process that hinders with the treatment of the Overactive bladder:
“Part of normal aging or everyday life”
“Not severe or frequent enough to treat”
“Too embarrassing to discuss”
“Treatment won’t help”
Treatment modalities are available- Do not hesitate in getting the treatments done
-
- Behavioural therapy– behavioural therapies are effective for treatment urge of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder. Beverly techniques are effective. Behavioural techniques are effective in community dwelling man and women. It includes Self-Management techniques, Timed or scheduled voiding and pelvic Floor muscle exercise.
a) Self-Management techniques:
While self-managing the urinary incontinence, the dietary Changes and fluid intakes should be monitored:
-
-
- Do not reduce the volume of fluids you are taking.
- Don’t drink fluids two hours before the bedtime.
- Avoid caffeine alcohol and nicotine.
- Weight loss is important.
- treat the constipation.
-
b) Timed or scheduled Voiding: This is done to train the bladder. It involves the process of:
Modification of boarding interval by 15-60 minute every 1-2 weeks until an acceptable voiding interval is achieved without incontinence and urge control – This is done by suppressing the urge using any of the following methods like keeping the body calm until urge subsides, Taking deep slow breath, Arm elimination the urge by mental calculation or mental imaging and contraction of pelvic floor muscle.
c) Pelvic floor training exercise– It consists of intermittent voluntary maximal contraction of pelvic floor muscles. It is shown that Continence has been improved six to 12 weeks after Pelvic floor muscle exercise.
Kegel exercise-Pelvic floor muscle exercise
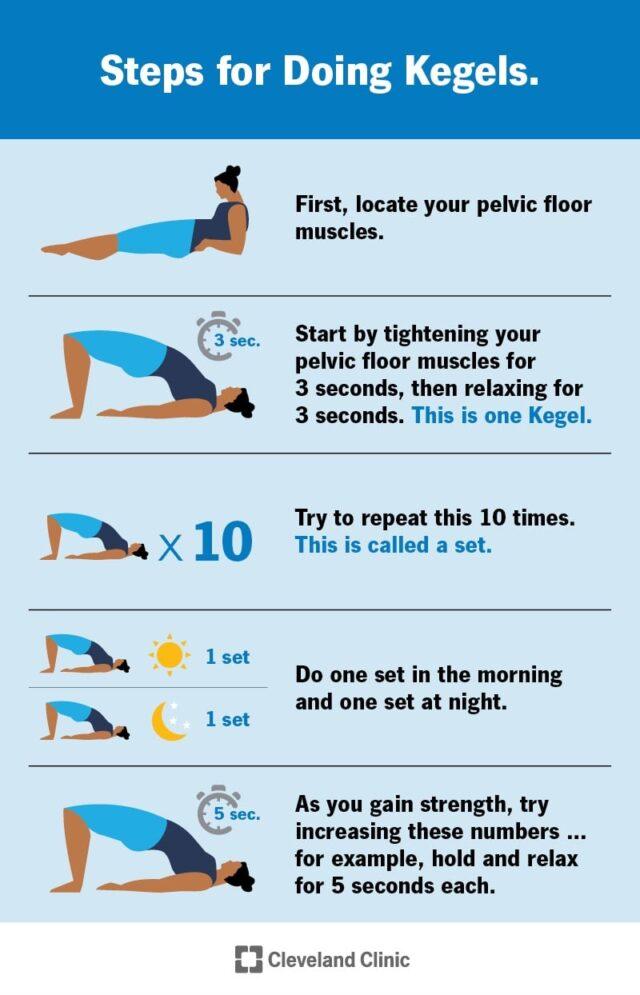
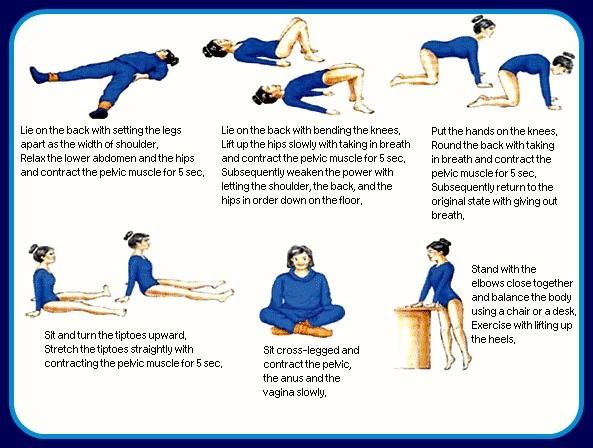
Pelvic floor muscle exercise
- Pharmacological medications are prescribed if patients are not benefitting on behavioural techniques. There are several drugs available such as Oxybutynin, Tolterodine, Solifenacin, Darifenacin and Trospium chloride.
- Surgical options are available such as augmentation enterocystoplasty and it is considered after failure of behavioral and pharmacological treatment.
Conclusion:
Incontinence can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to social withdrawal, depression, and decreased self-esteem. It’s crucial for individuals experiencing incontinence to seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause and explore appropriate treatment options. Treatments may include pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises) to strengthen the muscles, lifestyle changes, medications, medical devices, or, in severe cases, surgical interventions. If you or someone you know is dealing with incontinence, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to receive proper evaluation, guidance, and support. Many cases of incontinence can be managed or even resolved with the right approach and treatment.
Credits
Image: Freepik.com

